Google Groups
Spinnaker supports G Suite accounts (formerly Google Apps for Work) and Google Groups to manage authorization.
Fiat (Fix it Again Travis) is the authorization (authz) microservice of Spinnaker. It can grant access to users to execute pipelines, view infrastructure, etc. It is disabled by default. Much like authentication, Spinnaker allows for a variety of pluggable authorization mechanisms.
With Fiat, you can…
Permissions can be attached to applications and (provider) accounts. A permission associates a role with one of these
options: READ, WRITE, or EXECUTE (for apps only).
Keep these in mind as you consider your authorization strategy:
Fiat’s authorization model is an approve list that is open by default. In other words, when a resource does not define who is allowed to access it, it is considered unrestricted. This means:
Every permission in Spinnaker is granted to a role. Individual users cannot be granted permissions. You also grant Super admin access to a role. You may see discussions of users in Fiat’s implementation but it’s just an optimization in the storage to not recompute user → roles → permissions.
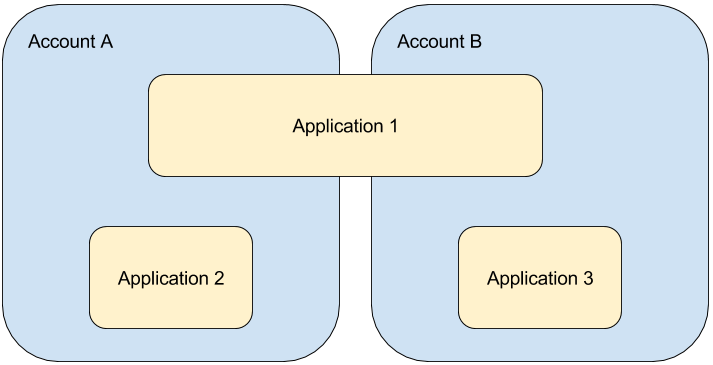
Account and application access control can be confusing unless you understand the core
relationship: accounts can contain multiple applications, and applications can span multiple
accounts. Giving access to an account does not grant access to the application and vice versa. Sometimes you need
both permissions to perform certain actions.
Authentication successfully setup in Gate.
Configured Front50 to use S3 or Google Cloud Storage (GCS) as the backing storage mechanism for persistent application configurations.
An external role provider from one of the following:
SAML roles are fixed at login time, and cannot be changed until the user needs to reauthenticate.
Enable the authorization feature.
Patience—there are a lot of small details that must be just right with anything related to authentication and authorization.
(Highly Suggested) All Spinnaker component microservices are either:
Firewalled off as a collective group, or:
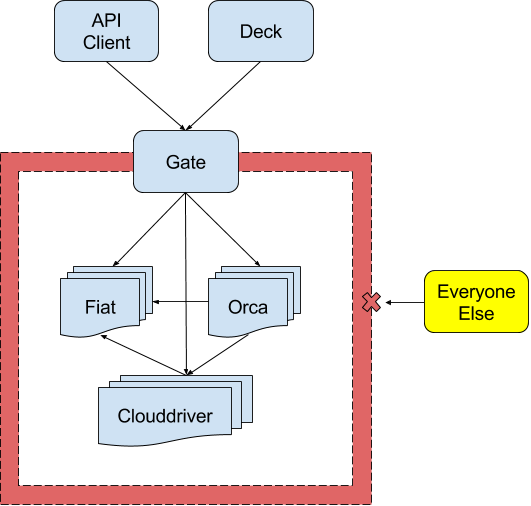
Use mutual TLS authentication:
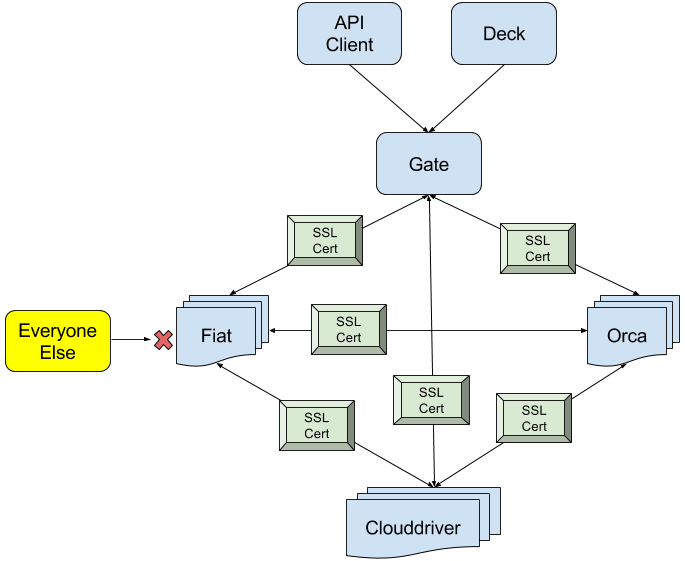
Because Clouddriver is the source of truth for accounts, Fiat reaches out to Clouddriver
to gather the list of available accounts. There are two types of access restrictions to an account: READ and
WRITE. Users must have at least one READ permission of an account to view the account’s cloud resources, and at
least one WRITE permission to make changes to the resources.
These halyard commands manage the READ and WRITE permissions.
PROVIDER= # Your cloud provider
hal config provider $PROVIDER account edit $ACCOUNT \
--add-read-permission role1 \ # Adds a READ permission
--add-write-permission role2 \ # Adds a WRITE permission
--remove-read-permission role3 \ # Removes a READ permission
--remove-write-permission role4 # Removes a WRITE permission
# Alternatively, you can overwrite the whole read or write list, comma delimited.
hal config provider $PROVIDER account edit $ACCOUNT \
--read-permissions role1,role2,role3 \
--write-permissions role1,role2,role3
Before Spinnaker 1.14, there were two types of restrictions to an application READ and WRITE.
In the 1.14 release, a new permission type called EXECUTE was added. For any new applications,
the permission required to trigger pipelines changes from groups with READ access to those with
EXECUTE access.
To maintain backward compatibility for existing applications, groups with READ access will implicitly
get EXECUTE access. There are two ways to change this behavior:
EXECUTE permissions to a group for an application: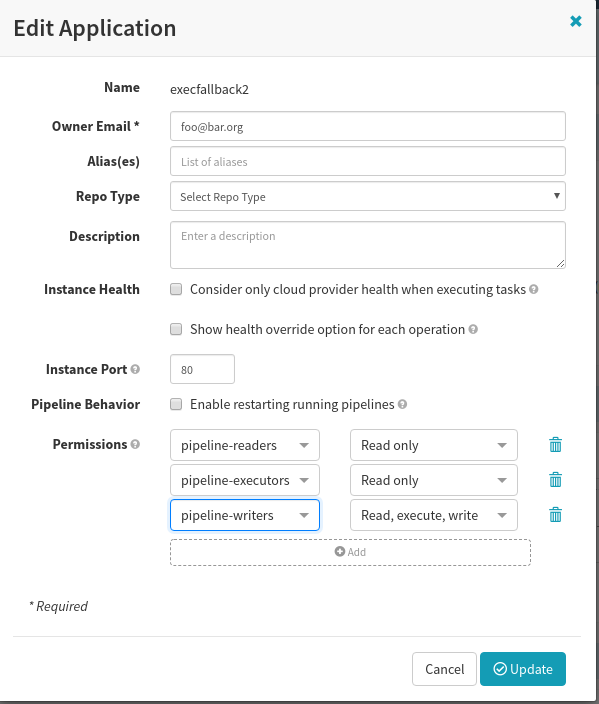
WRITE users implicit EXECUTE access by
setting the following property in fiat-local.yml: fiat.executeFallback: 'WRITE'
WRITE permission on the account.WRITE permission on that app.EXECUTE permission.EXECUTE on the app X and
WRITE on the account Y.In Spinnaker there are a few ways you can associate a role with a user:
EXTERNAL. They can be used in addition to authorization roles.In all these methods, users are referenced by a userId which is determined by the authentication method of your choice.
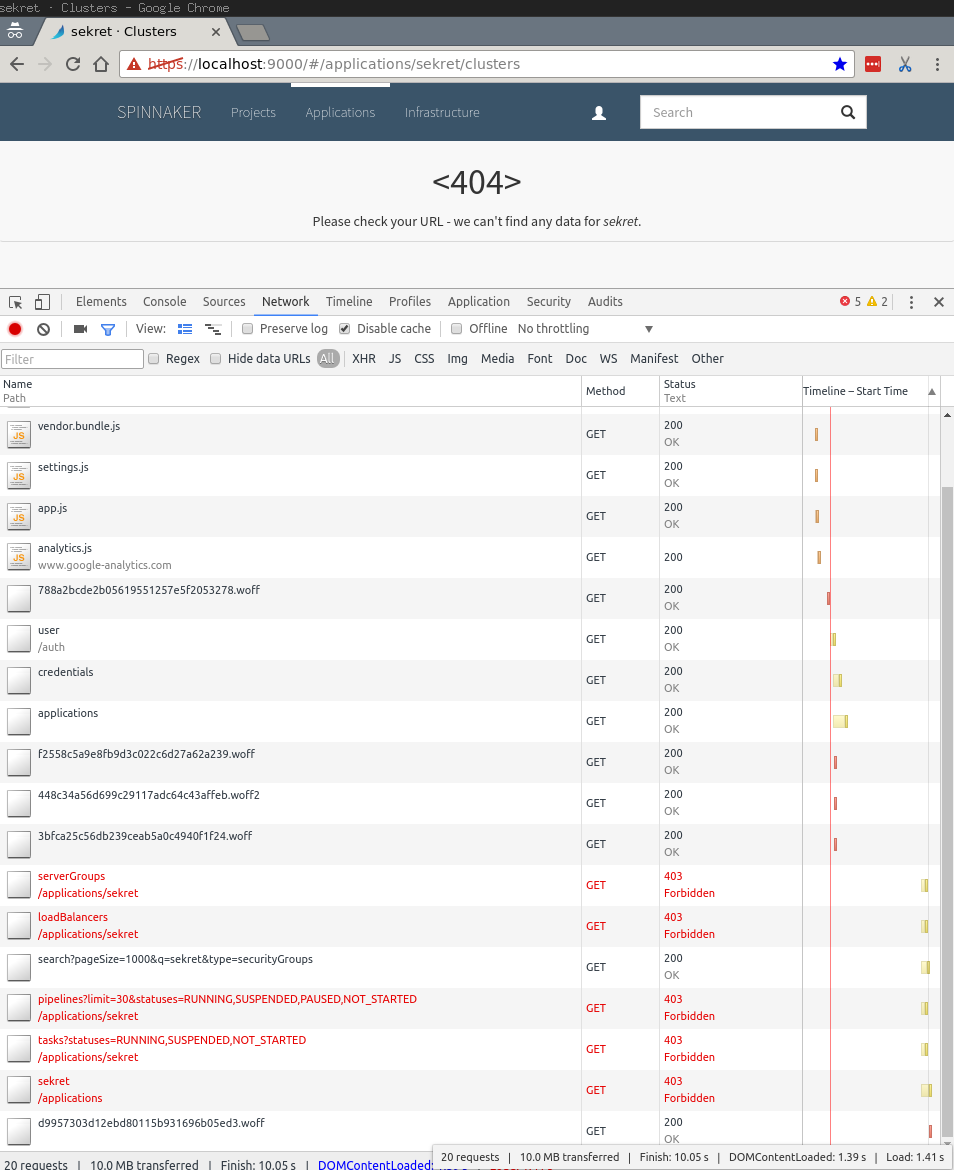
Because of the new access restrictions, https://localhost:9000/#/applications should no longer
list applications that have been restricted. Even navigating to the previously accessible page
should be denied:
A popular feature in Spinnaker is the ability to run pipelines automatically based on a
triggering event, such as a git push or a Jenkins build completing. When pipelines run against
accounts and applications that are protected, it is necessary to configure
them with enough permissions to access those protected resources. This can
be done in two ways:
Deeper details on Authorization in Spinnaker
Spinnaker supports G Suite accounts (formerly Google Apps for Work) and Google Groups to manage authorization.
Spinnaker supports using LDAP for authorization.
Pipeline permissions enable automatically triggered pipelines to modify resources in protected accounts and applications.
Spinnaker supports using SAML for authorization with certain conditions.
Service Accounts enable the ability for automatically triggered pipelines to modify resources in protected accounts or applications.
Spinnaker supports using GitHub teams for authorization. Roles from GitHub are mapped to the Teams under a specific GitHub organization.